Class PowerShellParser
- Namespace
- Alternet.Syntax.Parsers.Lsp.PowerShell
- Assembly
- Alternet.Syntax.Parsers.PowerShell.v10.dll
Represents a class that performs syntax and lexical analysis of specified PowerShell code text.
public class PowerShellParser : LspParser, IComponent, IDisposable, ISyntaxParser, IParser, ILexer, INotify, IUpdate, IImport, ILspDocumentProvider- Inheritance
-
PowerShellParser
- Implements
- Derived
Examples
Here is how to declare a PowerShellParser and assign it to the edit control from the C# code:
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var parser = new Alternet.Syntax.Parsers.Lsp.PowerShell.PowerShellParser();
var edit = new Alternet.Editor.SyntaxEdit();
edit.Parent = this;
edit.Lexer = parser;
string fileName = "myfile.ps1";
if (System.IO.File.Exists(fileName))
{
parser.FileName = fileName;
edit.LoadFile(fileName);
}
}
}
Here is how to declare a PowerShellParser and assign it to the edit control from the Visual Basic code:
Partial Public Class Form1
Inherits Form
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Sub Form1_Load(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs)
Dim parser = New Alternet.Syntax.Parsers.Lsp.PowerShell.PowerShellParser()
Dim edit = New Alternet.Editor.SyntaxEdit()
edit.Parent = Me
edit.Lexer = parser
Dim fileName As String = "myfile.ps1"
If System.IO.File.Exists(fileName) Then
parser.FileName = fileName
edit.LoadFile(fileName)
End If
End Sub
End Class
Remarks
PowerShellParser is a non-visual component designed to perform syntax highlighting for the PowerShell language. This LangServer-based parser relies on the PowerShell Language server to provide features like full syntax and analysis of the PowerShell code. When linked to the SyntaxEdit or TextEditor controls, this parser drives additional features such as code completion, code outlining, and underlying syntax errors and warnings.
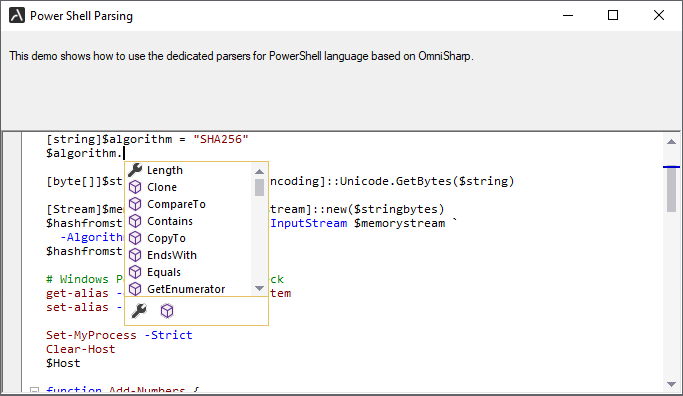
Here are some of the essential features provided by the PowerShellParser:
- Syntax Highlighting
- IntelliSense (Code completion)
- Code Outlining
Constructors
- PowerShellParser()
Initializes a new instance of the
PowerShellParserclass with default settings.
- PowerShellParser(IContainer)
Initializes a new instance of the
PowerShellParserclass with specified container.
Fields
- DefaultPowerShellCodeCompletionChars
Represents a default collection of characters that initializes a code completion procedure when typing.
- DefaultPowerShellDelimiters
Represents a default collection of delimiter characters.
- DefaultPowerShellSmartFormatChars
Represents a default collection of characters that initializes a smart formatting procedure when typing.
- DefaultPowerShellSyntaxOptions
Represents default set of flags determining syntax parsing and formatting behavior.
Properties
- CaseSensitive
Gets or sets a boolean value that indicates whether
SyntaxParsershould perform case-sensitive analysis of its content.
- Repository
Gets a
PowerShellRepositorythat holds methods for code completion purposes.
Methods
- CreateRepository()
Creates
ICodeCompletionRepositoryto perform code completion functionality for this parser.
- FindDeclaration(Point, bool)
Finds the declaration node at given position.
- IsCodeCompletionChar(char, byte, ref int)
Returns boolean value indicating that given character initializes a code completion procedure when typing.
- ResetCodeCompletionChars()
Resets
CodeCompletionCharsto the default value.
- ResetOptions()
Resets
Optionsto the default value.
- ResetSmartFormatChars()
Resets the
SmartFormatCharsto the default value.
- ShouldSerializeCodeCompletionChars()
Indicates whether the
CodeCompletionCharsproperty should be persisted.
- ShouldSerializeOptions()
Indicates whether the
Optionsproperty should be persisted.
- ShouldSerializeSmartFormatChars()
Indicates whether the
SmartFormatCharsproperty should be persisted.